5G ON-OFF Loops in the Wild
What are 5G ON-OFF Loops?
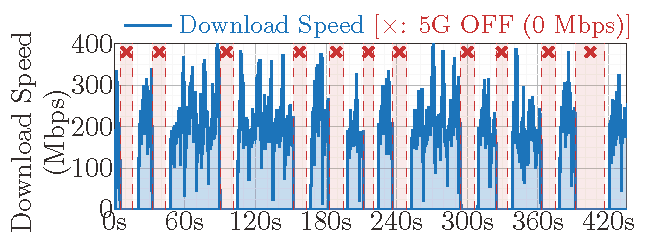
In operational 5G networks, a mobile device often loses its 5G radio access when there are no noticeable changes to its 5G radio channels. In these cases, 5G radio access is often recovered but is later lost again. As a result, 5G radio access enters an ON-OFF loop where radio access persistently oscillates between two states: 5G ON and 5G OFF, which significantly hurts data performance and even suspend data service (Figure 1).
An In-Depth Look into 5G ON-OFF Loops in the Wild (IMC'25)
We have released our 5G ON-OFF datasets on GitHub. We conducted extensive measurement experiments with all three major operators (T-Mobile, AT&T, Verizon) in 11 test areas in two U.S. cities: West Lafayette and Lafayette, from December 2024 to May 2025. We ran static experiments with bulk file download at selected locations and use Network Signal Guru to collect cellular messages. In total, we collected more than 2,000 loop instances.
Based on collected dataset, we have conducted an in-depth study on 5G ON-OFF loops, and we have published our results in IMC'25 paper “An In-Depth Look into 5G ON-OFF Loops in the Wild” . We analyzed prevalence and performance impact of 5G ON-OFF loops in operational 5G networks. 5G ON-OFF loops are commonly observed in operational 5G networks. Loops are observed in around half of the runs with all three operators (T-Mobile: 48.8%, AT&T: 51.1%, Verizon: 51.7%). Besides, the likelihood of 5G ON-OFF loops exceeds 50% at more than half of the locations in 8 out of 11 test areas. At these locations, 5G ON-OFF loops occur quite often every several tens of seconds and significantly hurts data performance and may even suspend data services.
We further identified the root causes of 5G ON-OFF loops. Although there are three different types of 5G ON-OFF loops observed in the wild (Figure 2, 5G SA: S1, 5G NSA: N1 and N2), all types of 5G ON-OFF loops share one common cause: the triggers to turn 5G ON and OFF can co-exist under (quasi-) same network conditions. Specifically, 5G cells are added because their RSRP/RSRQ measurements meet the pre-configured criteria. However, turning 5G OFF is not always associated with RSRP/RSRQ measurement events. Consequently, loops are created with inconsistent ON/OFF triggering conditions (Table 1). Please refer to our paper for more details of our 5G ON-OFF loops study.
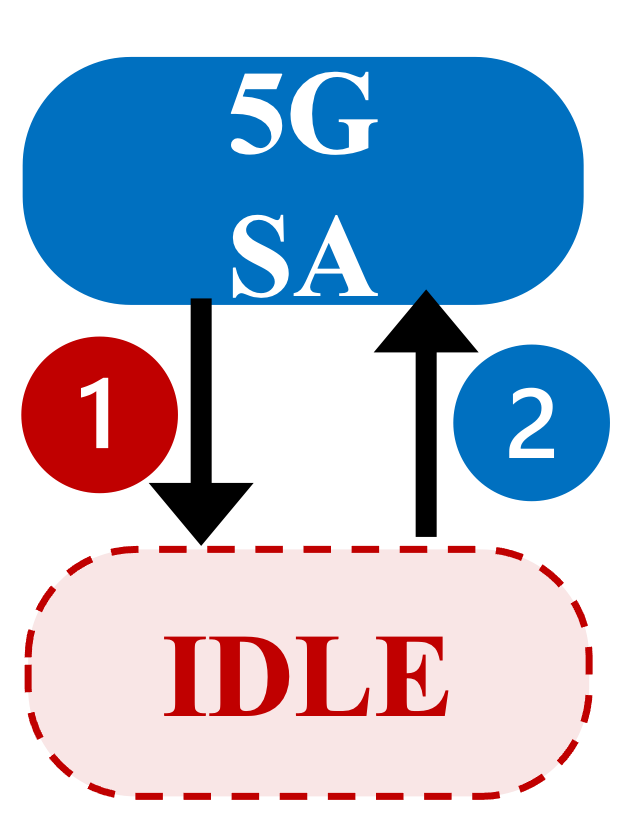
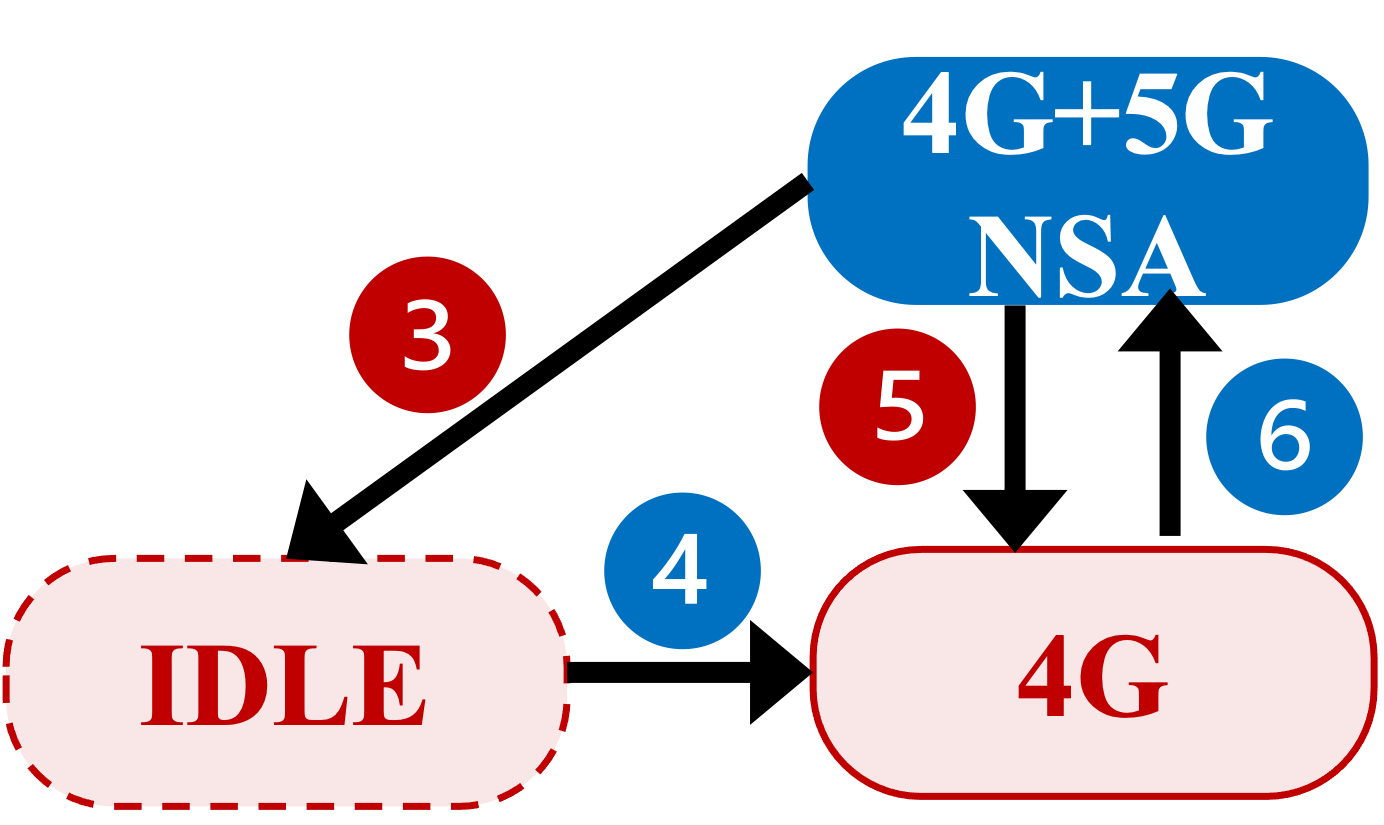
Figure 2 Three 5G ON-OFF loop types

Study 5G ON-OFF Loops by Yourself!
If you are interested in the problem of 5G ON-OFF loops, you have two options to investigate this problem by yourself:
Option 1: Use open dataset
We released our collected 5G ON-OFF datasets here. It contains the traces of 5G ON-OFF events as well as other important information such as location, radio condition and throughput. Please refer to README in the dataset for more details.
Option 2: Collect data by yourself
We strongly encourage you to collect your own 5G ON-OFF dataset for analysis. Below are instructions to run “5G ON-OFF” experiments using mperf-any, one task supported by MI-LAB. If you need any technical support, please contact us at milab@cs.purdue.edu.
- Step 1: install mperf-any. Please refer to the guideline.
-
Step 2: run mperf-any. Please refer to the
guideline.
In summary, you need to do three (four) things.- Start. Start running this task at test locations where you want to conduct experiments over 5G networks (stationary experiments recommended).
- Stop. Stop this task whenever you want (likely after completing the experimentation time).
- Check. (optional but strongly recommended). Check if the task runs normally when it is running.
- Upload. It supports offline data uploading after you finish one or many taskrounds.
- Tips and more information
- Network access setup (one-time effort). Please enable mobile data and disable WiFi.
- Register your own account (recommended). You can use GUEST or usernames provided by the MI-LAB team (username: mssn_5g1, password: MSSN_2025_5Gmeas).
- Run stationary experiments at selected locations to avoid the impact of environmental and radio dynamics. We encourage to use other apps to check the serving cells over time (to check whether 5G ON-OFF switches occur).
- Please run each experiment for 3-5 minutes or longer to capture multiple ON-OFF switches if applicable.
- We recommend using file downloading as the default traffic load. If you want to test with other applications such as video or live streaming, change traffic setting to ping in mperf_any and run the target apps on the test phone.
- Step 3: view (and download) data. Data logs will be available on your test phone and on MI-LAB if uploaded.